Explore the RNA Methylome with SYSY Antibodies
SYSY is the first commercial supplier of m6A specific antibodies. Their products have been used in more than 700 scientific publications, and enabled the development of entirely new methods for researching the RNA methylome. The development of monoclonal and recombinant antibody variants complements the extremely successful polyclonal anti-m6a antibody and guarantees best reproducibility and lot-to-lot consistency. The anti m6A antibodies are suitable for a broad panel of applications like MeRIP, m6A-CLIP and miCLIP sequencing, classical IP, dot blotting, and ELISA.
m6A Antibodies
| Cat No. | Product Description | Application |
| 202-003-SY | m6A, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purified | Dot blot IP MeRIP |
| 202-008-SY | m6A, rabbit, monoclonal, recombinant IgG | Dot blot IP MeRIP |
| 202-011-SY | m6A, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgG | Dot blot IP MeRIP |
| 202-018-SY | m6A, rabbit, monoclonal, recombinant IgG | Dot blot IP MeRIP |
| 202-111-SY | m6A, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgG | Dot blot IP MeRIP |

Figure 1: Posttranscriptional RNA methylation and demethylation are carried out by writers (METTL complex) and erasers like FTO. The resulting site-specific RNA modifications influence further RNA processing, translation and stability.
Exploring the spliceosome, where everything began
In 1987, Peter Bringmann and Reinhard Luehrmann developed the first polyclonal antibodies against m6A to investigate the relevance of this RNA modification in the eukaryotic spliceosome. These antibodies enabled the quantitative immunoisolation of m6A modified small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) U2, U4 and U6 from small nuclear riboproteins (snRNPs) (Bringmann, Lührmann, 1987).
In 1997, SYSY included the original m6A antiserum from R. Luehrmann and P. Bringmann in its catalogue and was the first commercial supplier of m6A specific antibodies.
Later it turned out that the N6-methyl adenosine or m6A modification is involved in many more post-transcriptional regulatory processes and the m6A methylome of the transcriptome emerged as an entirely new and rapidly growing field of research.
The key publications from Kate Meyer (Meyer et al., 2012) and Dan Dominissini (Dominissini et al., 2012 and 2013) paved the way for the worldwide success of our affinity purified version of the m6A rabbit polyclonal antibody (cat. no. 202 003). Meyer and Dominissini have developed the antibody based m6A-sequencing method, an approach based on parallel sequencing of immunoisolated RNA fragments (100 -200 nt long) carrying m6A modifications (figure 2).
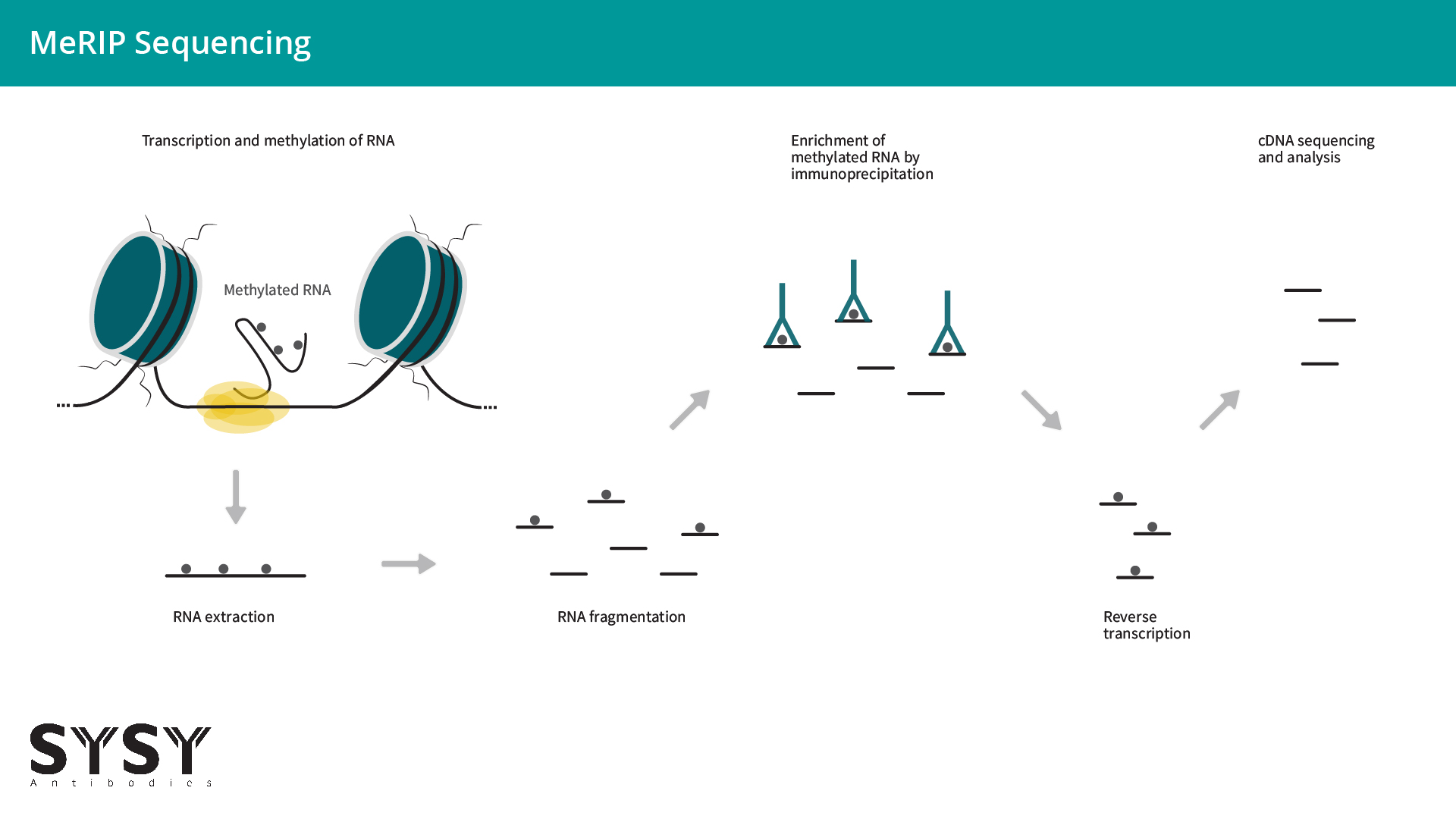
Figure 2: MeRIP seq is based on the parallel sequencing of immunoisolated m6A modified RNA fragments.
This new technique, also called MeRIP sequencing, allowed scientists to uncover numerous posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms, all of which are modulated by m6A modifications, leading to a constantly growing number of scientific publications (figure 3).
